At the beginning of 2023, international pharmaceutical giant GSK announced that it would abandon investment in the field of cell and gene therapy and shift its focus to the field of small nucleic acid drugs. This news quickly attracted public attention and enthusiasm. In fact, as early as December 2022, GSK reached a cooperation agreement with Wave Life Sciences, a nucleic acid therapy research and development company, investing a total of 3.3 billion US dollars to accelerate the development of small nucleic acid drugs. This cooperation has brought GSK at least eight projects forward. So, what is a small nucleic acid drug? Why is it favored by giants? How is the research progress in China?
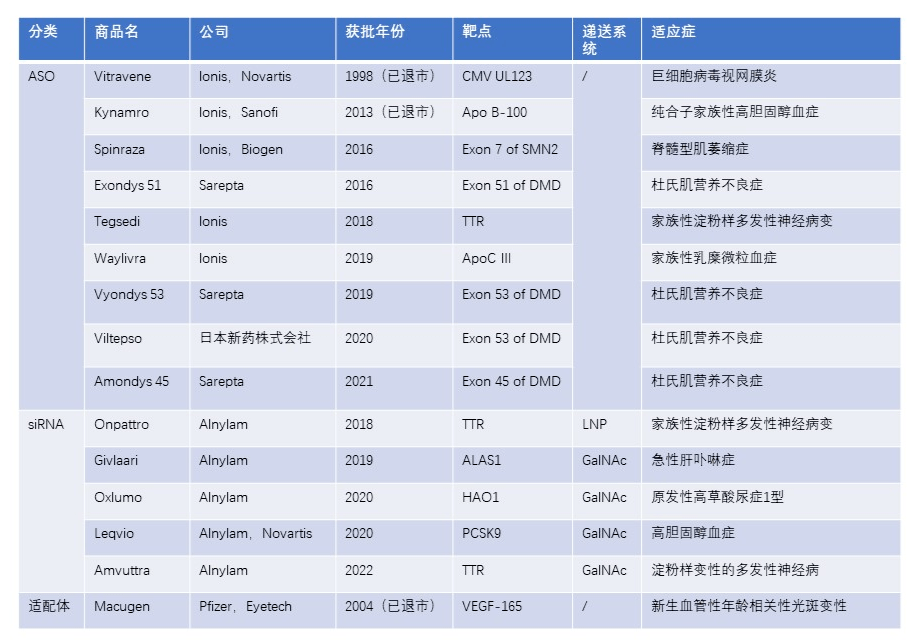
What is a small nucleic acid drug?
Small nucleic acid drugs refer to nucleotide sequences with no more than 30 base pairs, and their mechanism of action is to act on mRNA through specific nucleotide sequences, thereby inhibiting the expression of target proteins and achieving the effect of treating diseases. Small nucleic acid drugs include various types such as RNA small interfering drugs (siRNAs), antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), microRNAs (miRNAs), small activated RNAs (saRNAs), mRNA, RNA aptamers, etc. Small nucleic acid drugs can be used for treatment at the post transcriptional level, targeting specific protein targets that are difficult to develop into drugs, and have the potential to develop treatments for "untreatable" diseases, with significant clinical significance.
In addition, small nucleic acid drugs can directly regulate protein expression, overcoming the problem of potential drug resistance in targeted protein drugs, and have the potential to achieve disease cure, with the potential to treat symptoms and root causes. Unlike traditional small molecule drugs and antibody drugs, small nucleic acid drugs only need to design corresponding RNA fragments for pathogenic gene sequences, without recognizing the spatial conformation of proteins. Therefore, small nucleic acid drugs have the advantages of short development cycles, fast drug target screening, clear mechanisms of action, and high success rates.
According to a report released by research firm Research And Markets, the global small nucleic acid drug market reached $6.1 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow to $19.9 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate of 15.9%. Considering the numerous advantages and vast market space of small nucleic acid drugs, industry insiders predict that small nucleic acid drugs will become an important competitive field in the global pharmaceutical industry.
How is the progress of domestic research and development?
Currently, the research and development of small nucleic acid drugs in China is in a rapid development stage. With the successful commercialization of the first batch of small nucleic acid drugs abroad, domestic pharmaceutical companies have also joined the field of small nucleic acid drug research and development, such as Sanuo Pharmaceutical, Ruibo Biology, Yuekang Pharmaceutical, Tengshengbo Pharmaceutical, Qilu Pharmaceutical, Xingyao Kunze, etc.
Founded in 2007, Sanofi Pharmaceuticals is one of the earliest companies in China to develop small nucleic acid drugs. The company adopts a unique peptide nanoparticle delivery system, which uses essential amino acids in the human body to package small nucleic acid drugs, ensuring safety and stable delivery of drugs to target cells, thereby effectively inhibiting target genes. At present, the company's research and development pipeline covers fields such as tumors, skin diseases, and liver diseases. The company's core product STP705 and its upgraded version STP707 achieve local treatment and systemic administration effects through the use of different peptide nanocarriers. STP705 has entered Phase II clinical trials.
Ruibo Biotechnology was also established in 2007, dedicated to the innovation of small nucleic acid technology and the research and development of small nucleic acid drugs. The company's anti hepatitis B siRNA drug RBD1016 has shown in preclinical studies that it can not only inhibit the replication of hepatitis B virus DNA, but also effectively and persistently reduce the level of HBsAg, with good safety and expected pharmacokinetic properties. Currently, RBD1016 is undergoing Phase I clinical trials.
Yuekang Pharmaceutical has been involved in the field of nucleic acid since 2021, dedicated to the research and development of small nucleic acid drugs and mRNA vaccines. The company's fastest growing small nucleic acid drug is CT102, an ASO drug that targets the human insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor (IGF1R) gene for the treatment of primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Currently, CT102 is undergoing phase IIa clinical trials. The results of the Phase I clinical trial indicate that CT102 has good safety and tolerability, and no adverse reactions leading to drug discontinuation or subject withdrawal have occurred.
At present, domestic small nucleic acid drugs are still in the initial research stage, and the industry generally believes that in three to four years, domestic small nucleic acid drugs are expected to achieve commercialization.
As a drug with disruptive technology, small nucleic acid drugs have multiple advantages, including a wide range of drug targets, applicability to a wide range of disease fields, long-lasting efficacy and short research and development cycles, and fast production speed. This makes small nucleic acid drugs have enormous development potential in fields such as combating infectious diseases, treating rare and chronic diseases. With the continuous breakthroughs and innovations in the application field and technology of small nucleic acid drugs, their market demand and scale will continue to expand. With the continuous advancement of technology, small nucleic acid drugs are expected to become the third wave of modern new drugs, following small molecule drugs and antibodies.